Feet-Relief is supported by our audience. When you purchase through one of our links, we may earn a small affiliate commission. As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.Your cost is not affected.
Managing Peripheral Neuropathy Both Feet Or One:
Find Relief with our tips
Peripheral Neuropathy, both feet or one, affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the nerves that carry messages to and from the brain and spinal cord are damaged or diseased. Although it can affect any part of the body, it is most commonly seen in the feet. This leads to a variety of symptoms such as numbness, tingling, burning sensations, and even pain.
In this blog post, we explore what Peripheral Neuropathy is, its causes, diagnosis, treatment options, preventive measures, and how regular exercise can help in managing it. We also discuss how to live with this condition including self-care tips and when to seek medical attention.
If you or someone you know has been diagnosed with Peripheral Neuropathy or experiences any of these symptoms in their feet, read on for some relief!
Understanding Peripheral Neuropathy both feet or one
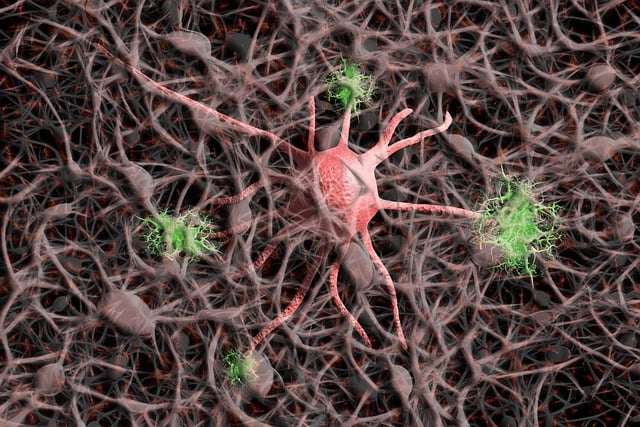
Peripheral neuropathy affects the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord. Symptoms range from numbness to muscle weakness. Damage to the peripheral nerves causes pain, tingling, or loss of sensation. The most common causes of peripheral neuropathy include diabetes, autoimmune diseases, and traumatic injuries.
Proper diagnosis is important for effective treatment. Sensory nerves and autonomic nerves are involved, and a wide range of factors, including kidney disease and carpal tunnel syndrome, can contribute to severe cases of neuropathic pain. Neuropathy my affect other parts of your body as it progresses.
Additionally, there are different types of nerves with their own specific functions. Extensive medical history helps identify underlying causes. Prompt diagnosis allows for early intervention and management of peripheral neuropathy.
An Overview of the Peripheral Nervous System
The peripheral nervous system comprises a network of nerves that connect the central nervous system to various parts of the body, including both feet. These nerves play a crucial role in controlling muscle movement, sensory function, and autonomic functions like blood pressure regulation.
When the peripheral nerves are damaged, it leads to peripheral neuropathy. This manifests as symptoms such as pain, numbness, and muscle weakness. Although the medical problems often appear in your own feet, they may affect the rest of the body, as well.
Peripheral neuropathy can have various causes, ranging from diabetes and vitamin deficiencies to autoimmune diseases. Treatment options for peripheral neuropathy focus on managing symptoms, addressing underlying causes, and promoting nerve health.
Recognizing Symptoms of Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy can manifest in various symptoms, depending on the type of nerve damage and underlying cause. These can include pain, numbness, tingling, muscle weakness, and coordination problems.
For instance, diabetic neuropathy often affects the feet, leading to a loss of sensation, foot ulcers, and an increased risk of infection. Rheumatoid arthritis can also cause peripheral neuropathy, resulting in pain, swelling, and joint deformity.
If you experience any of these symptoms, seeking prompt medical attention is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment to prevent further complications.
Causes of Peripheral Neuropathy in Feet
Peripheral neuropathy in the feet can have various causes. Diabetes is a common culprit, particularly when it comes to sensory neuropathy. Other potential causes include autoimmune diseases, vitamin deficiencies, and traumatic injuries. Heavy metals, certain medications, and genetic conditions can also contribute to peripheral nerve damage.
Proper foot care, blood sugar management, and a healthy diet can play a crucial role in prevention and management. Identifying the underlying cause is essential for determining the most effective treatment approach.
Diabetes as a Major Contributor
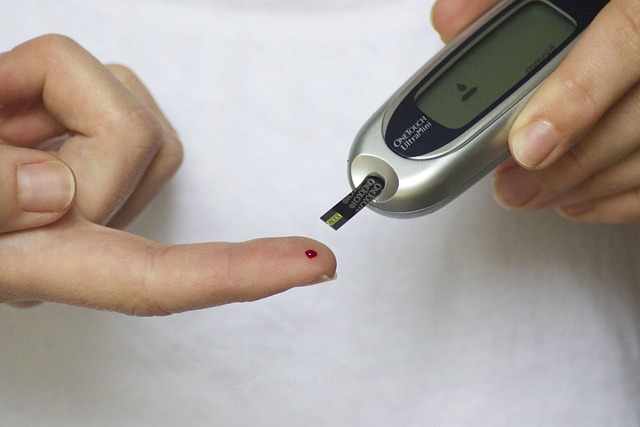
Diabetes is the leading cause of peripheral neuropathy, especially in the feet. High blood sugar levels can damage the nerves, resulting in symptoms such as numbness, pain, and muscle weakness. Effective management of diabetes, including careful blood sugar control, regular medical monitoring, and proper foot care, is crucial in preventing and managing diabetic peripheral neuropathy.
A healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet, regular exercise, and blood pressure control can also help minimize the risk of developing this condition. Early detection and treatment are essential for preventing complications like foot ulcers and amputation.
Other Potential Causes
Peripheral neuropathy in the feet can be caused by conditions other than diabetes. Autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis can lead to nerve damage and symptoms of peripheral neuropathy. Traumatic injuries, nerve compression, and certain medications can also contribute to peripheral nerve damage.
Identifying the underlying cause is crucial for determining the most effective treatment approach. Collaborating closely with a healthcare professional can help uncover the cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Diagnosis of Peripheral Neuropathy
Early detection and diagnosis of peripheral neuropathy are crucial for effective treatment. A physical exam, medical history, and neurological tests are common diagnostic methods.
Nerve conduction studies and electromyography can assess nerve function, while blood tests, imaging, and nerve biopsies may help identify underlying causes. Prompt medical attention is vital to prevent complications.
The Importance of Early Detection and Diagnosis
Early detection of peripheral neuropathy allows for timely treatment, reducing the risk of complications. Delayed diagnosis can lead to more nerve damage, increased pain, and decreased quality of life. Recognizing symptoms and seeking medical attention are crucial steps in the diagnostic process.
Diagnostic tests, physical exams, and medical history reviews help healthcare professionals accurately diagnose peripheral neuropathy. Collaborating with healthcare professionals ensures a timely and accurate diagnosis, leading to more effective treatment outcomes.
Diagnostic Tests for Peripheral Neuropathy
Diagnostic tests for peripheral neuropathy include nerve conduction studies, electromyography, blood tests, imaging (such as MRI or CT scans), and nerve biopsies. Nerve conduction studies measure the speed of nerve impulses to identify damage and the type of neuropathy.
Electromyography assesses muscle function, aiding in diagnosis. Blood tests detect underlying conditions that may cause neuropathy. Imaging identifies physical causes, and nerve biopsies provide further insights into the condition.
Treatment Options for Peripheral Neuropathy
Managing peripheral neuropathy involves various treatment options that focus on symptom management, addressing underlying causes, and promoting nerve health. Medications, including pain relievers, anti-seizure drugs, and antidepressants, can help manage symptoms.
Physical therapy, exercises, and lifestyle modifications can improve muscle weakness, coordination, and pain management. Treating underlying conditions, such as diabetes or autoimmune diseases, can alleviate symptoms. Alternative therapies like acupuncture or nerve stimulation may provide additional relief.
Treating the Underlying Cause
To effectively treat peripheral neuropathy in both feet, it is crucial to identify and address the underlying cause. This may include conditions like diabetes or vitamin deficiencies. Consulting with a healthcare provider will help develop a comprehensive treatment plan that targets the root cause.
Additionally, incorporating lifestyle changes such as exercise and a healthy diet can promote overall health. Medications, such as pain relievers and topical creams, can alleviate symptoms, and alternative therapies like acupuncture or physical therapy may provide further relief.
Medications to Alleviate Symptoms
To alleviate symptoms of peripheral neuropathy in both feet, there are various medications that can be used. For mild symptoms, over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen and ibuprofen can provide relief.
More severe pain can be managed with prescription medications such as gabapentin and pregabalin. Topical treatments like lidocaine patches and capsaicin cream can offer localized relief. Antidepressants like amitriptyline can help manage both pain and depression associated with peripheral neuropathy.
In rare cases of severe pain, opioids may be prescribed, but caution should be exercised due to the risk of addiction and other side effects.
Non-Medical Treatments and Therapies
Regular exercise can improve blood flow and reduce symptoms of peripheral neuropathy. Proper foot care, including regular washing, moisturizing, and checking for injuries, can prevent complications. Hot and cold therapy, such as using warm water or ice packs, can provide temporary relief. Massage and acupuncture may be beneficial in reducing symptoms.
Lifestyle changes, such as reducing alcohol consumption and quitting smoking, can improve overall health and manage symptoms.
Preventive Measures
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle by following a balanced diet and engaging in regular exercise is crucial in preventing peripheral neuropathy. It’s also important to wear properly fitting shoes with adequate support and cushioning to protect the feet.
Avoid exposing your feet to extreme temperatures and manage underlying health conditions like diabetes or vitamin deficiencies. Practicing good foot hygiene and regularly inspecting your feet for any signs of injury or infection are essential preventive measures.
Lifestyle Changes for Prevention
Incorporating regular physical activity into your daily routine can enhance blood circulation, reducing the risk of developing peripheral neuropathy. Additionally, maintaining a nutrient-rich diet can help safeguard against nerve damage while promoting overall health.
Avoiding alcohol and smoking are other beneficial measures to minimize the chances of nerve damage. Taking care of your feet, including wearing comfortable shoes and conducting regular inspections, can prevent potential complications.
Lastly, managing underlying conditions such as diabetes or autoimmune disorders can significantly contribute to the prevention of peripheral neuropathy.
Regular Check-ups and Monitoring
Regular check-ups and monitoring are essential for managing peripheral neuropathy. They help identify any changes in symptoms or the progression of the condition. It’s important to keep track of daily activities and potential triggers that may worsen symptoms.
Making lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise and a healthy diet, can improve overall health and potentially alleviate symptoms. Medications like pain relievers and nerve pain medications may be prescribed to manage symptoms. Alternative therapies like acupuncture or transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) may also provide relief.
How Can Regular Exercise Help in Managing Peripheral Neuropathy?
Regular exercise plays a crucial role in managing peripheral neuropathy by improving blood flow, nerve function, and muscle strength. It can reduce pain, enhance balance, and increase mobility. Low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling are recommended to minimize further nerve damage.
Working with a physical therapist can provide guidance on the right exercise program.
How common is this condition?
Peripheral neuropathy is a prevalent condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It can be caused by various factors such as diabetes, chemotherapy, and alcoholism. Some common symptoms include numbness, tingling, and burning sensations in the feet. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing symptoms and preventing further nerve damage.
Motor symptoms
When managing peripheral neuropathy in both feet, it’s important to work with a healthcare professional to develop a comprehensive treatment plan. This may include medications to alleviate symptoms, physical therapy to improve mobility, and lifestyle changes to promote overall foot health.
Good foot hygiene, such as daily washing and drying, along with wearing clean and dry socks, can help prevent infections. Choosing supportive footwear that fits well and provides cushioning is also essential. Incorporating low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling can improve circulation and reduce pain.
Additionally, alternative therapies like acupuncture or massage can complement traditional medical treatments.
Sensory symptoms
Identifying the underlying cause of peripheral neuropathy is crucial in managing sensory symptoms. Good foot care, including wearing comfortable shoes and regularly inspecting your feet, is essential.
Regular exercise improves circulation and reduces nerve pain. Alternative therapies like acupuncture or massage therapy can provide additional relief. Working with a healthcare professional to find the right medications for symptom management is important.
By addressing these sensory symptoms, you can effectively manage peripheral neuropathy in both feet.
Autonomic symptoms
Managing autonomic symptoms of peripheral neuropathy can significantly improve your quality of life. These symptoms, such as changes in blood pressure, are a common manifestation of peripheral neuropathy.
Understanding and addressing these autonomic symptoms are crucial for effective management. Treatment options may include medication, lifestyle changes, and other interventions. Consult with your healthcare provider to develop a comprehensive plan that addresses your specific autonomic symptoms.
Outlook / Prognosis
The prognosis for peripheral neuropathy can vary depending on the underlying cause and individual response to treatment. Early diagnosis and intervention can lead to better long-term outcomes. With proper management, many people experience improved symptoms and function.
Regular medical care, lifestyle modifications, and adherence to the treatment plan can positively impact the prognosis. Staying informed about advancements in peripheral neuropathy management is crucial for optimizing your outlook.
Living With
Living with peripheral neuropathy necessitates adopting strategies to manage symptoms and enhance overall well-being. Implementing healthy lifestyle choices, such as regular exercise and a balanced diet, supports nerve health and mitigates peripheral neuropathy symptoms.
Engaging in pain management techniques like physical therapy or alternative therapies alleviates peripheral neuropathy symptoms. Seeking emotional support through therapy or support groups addresses the psychological impact. Developing a comprehensive care team aids in effective management of peripheral neuropathy.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I take care of myself?
To take care of yourself with peripheral neuropathy, focus on proper foot care, blood sugar management, and a healthy lifestyle. Regularly check your feet, wear comfortable shoes, and practice good foot hygiene.
Manage blood sugar levels to prevent further nerve damage. Follow a balanced diet and engage in physical activity under healthcare guidance for improved nerve function.
When should I see my healthcare provider, or when should I seek care?
If you’re experiencing symptoms like numbness, pain, or muscle weakness in both feet, it’s important to consult your healthcare provider. Prompt care can help identify the underlying cause and initiate appropriate treatment.
Regular follow-ups are crucial for monitoring the progression of peripheral neuropathy. Reach out to your healthcare provider with any concerns or questions about your symptoms.
Living with peripheral neuropathy
Managing peripheral neuropathy in both feet requires a comprehensive approach that includes understanding the condition, identifying its causes, seeking early diagnosis, exploring treatment options, and adopting preventive measures.
While medications can help alleviate symptoms, addressing the underlying cause is essential for long-term relief. Non-medical treatments and therapies can also provide significant benefits in managing peripheral neuropathy.
Additionally, making lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise and maintaining good foot care, can play a crucial role in managing the condition. It’s important to monitor your symptoms, seek regular check-ups, and consult with your healthcare provider for proper guidance and care.
By taking proactive steps and staying informed, individuals with peripheral neuropathy can improve their quality of life and find relief from the associated discomfort.
Amazon and the Amazon logo are trademarks of Amazon.com, Inc, or its affiliates.